In the forever-evolving sphere of health and welfare, new buzzwords usually emerge, leaving many of us gaping at what they mean. One term that has acquired consideration in current years is NAD or Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide.
While it might sound like a portion, this coenzyme plays a critical act in our body’s fundamental systems. Let us delve into what is nad, its functions, and why it is suitable for a topic of interest.
The Basics of NAD
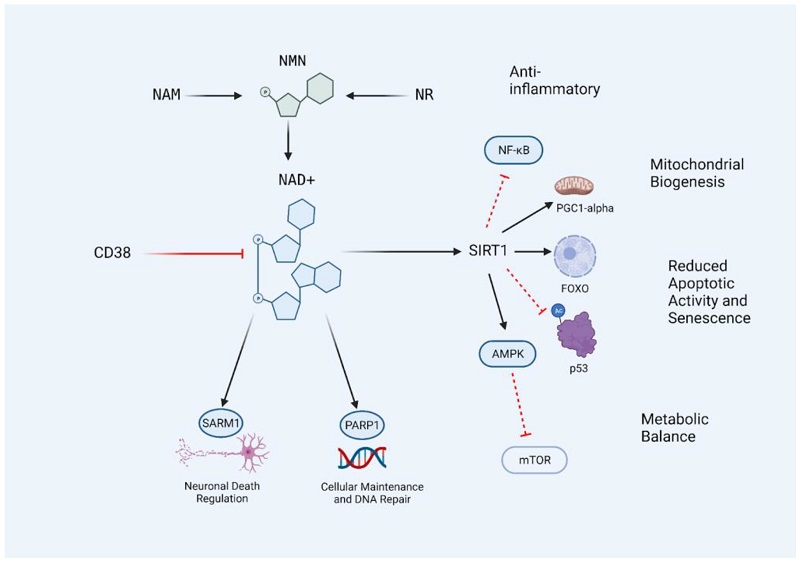
NAD bears Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, a coenzyme in the direction of all living cells. It comes from niacin, a type of vitamin B3, and is important for the proper working of our cells. NAD exists in two modes: NAD+ and NADH. The plus and extended signs denote the molecule’s decomposition states, which are fundamental in the process of developing nutrients into an element.
The Role of NAD in the Body
At its center, NAD is vital for absorption, the process by which our bodies convert what we eat and drink into strength. It acts as a cofactor for enzymes involved in redox reactions – chemical responses that transfer electrons between fragments. This process is critical for create ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary strength currency of our cells.
Beyond energy results, NAD also plays a meaningful role in:
· DNA Repair:
NAD is complicated in the repair of damaged DNA, helping to maintain the completeness of our genetic material.
· Gene Expression:
It influences the exercise of proteins called sirtuins, which regulate gene expression and are connected to aging and endurance.
· Cellular Défense:
NAD helps in managing oxidative stress, a condition from excessive free radicals that can damage cells and tissues.
Why is NAD Important?
The significance of NAD cannot be exaggerated, exceptionally considering its difficulty in a roomy range of organic processes. As we age, the levels of NAD+ in our bodies likely to decrease. This decline is guided by differing age-connected fitness issues, including dropped off energy levels, cognitive decline, and raised susceptible Ness to diseases.
NAD and Aging
Research has proved that pushing NAD levels in the body take care of potentially hinder the aging process.
Conclusion
Its part in processes such as DNA repair, gene expression, and basic defines underlines its significance to our health. While the prospect of NAD as a key to durability is exciting, it is owned by staying informed accompanying the latest controlled findings and approach supplementation accompanying care.
Ultimately, understanding NAD empowers us to appreciate the elaborate workings of our parties and the potential pathways to enhancing our strength as we age. While not essential for everyone, the survey of NAD remains an irresistible area of study accompanying the promise of unlocking new insights into human fitness and wellness.