Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) has revolutionized the field of medicine, offering patients safer and more efficient alternatives to traditional open surgery. With advancements in technology and surgical techniques, MIS is becoming the preferred choice for many medical procedures. This article explores the benefits, types, and future trends of minimally invasive surgery, highlighting its role in shaping the future of medical procedures.
What is Minimally Invasive Surgery?
Minimally invasive surgery involves performing operations through small incisions using specialized instruments and techniques. Unlike traditional open surgery, which requires large cuts, MIS uses tiny cameras, robotic systems, and precise instruments to minimize tissue damage and enhance recovery. Common types of minimally invasive surgery include laparoscopy, robotic surgery, and endoscopic surgery.
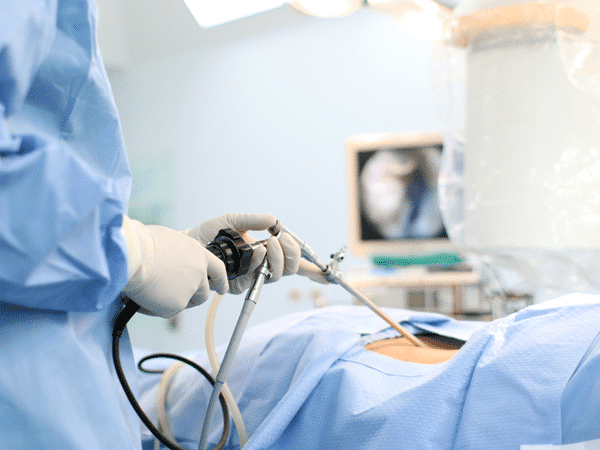
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Surgery
Reduced Pain and Scarring
One of the most significant advantages of minimally invasive surgery is the reduction in postoperative pain and scarring. Smaller incisions mean less tissue damage, which translates to less pain and quicker healing. Patients undergoing MIS often experience minimal scarring, as the small incisions require fewer stitches and heal more efficiently1.
Shorter Hospital Stays
MIS procedures typically result in shorter hospital stays compared to traditional open surgeries. Patients can often return home within a day or two, reducing the risk of hospital-acquired infections and lowering overall healthcare costs. This quick turnaround is particularly beneficial for patients with busy lifestyles or those who prefer to recover in the comfort of their own homes6.
Faster Recovery Times
The minimally invasive approach leads to faster recovery times, allowing patients to resume their normal activities sooner. This is especially important for individuals who need to return to work or care for their families. The reduced recovery period also means less time off from daily responsibilities and a quicker return to a normal routine5.
Types of Minimally Invasive Surgery
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is one of the most common forms of minimally invasive surgery. It involves the use of a laparoscope, a thin tube with a camera and light, to visualize the inside of the abdomen. Surgeons make small incisions and use specialized instruments to perform procedures such as gallbladder removal, hernia repair, and appendectomy1.
Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery is an advanced form of MIS that utilizes robotic systems to enhance precision and control. Surgeons operate robotic arms from a console, allowing for greater dexterity and accuracy. Procedures such as prostatectomy, hysterectomy, and heart valve repair are commonly performed using robotic surgery. The enhanced 3D visualization and precise movements reduce the risk of complications and improve surgical outcomes4.
Endoscopic Surgery
Endoscopic surgery involves the use of an endoscope, a flexible tube with a camera, to access and treat internal organs. This technique is widely used in gastrointestinal procedures, such as colonoscopy and gastroscopy, as well as in ENT (ear, nose, and throat) surgeries. Endoscopic surgery allows for detailed visualization and targeted treatment with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues1.
Future Trends in Minimally Invasive Surgery
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is set to play a significant role in the future of minimally invasive surgery. AI algorithms can assist surgeons in planning and executing complex procedures, enhancing precision and reducing the risk of errors. Machine learning models can analyze patient data to predict outcomes and optimize surgical techniques, leading to personalized and efficient treatments4.
Development of New Surgical Instruments
The continuous development of advanced surgical instruments is driving the growth of minimally invasive surgery. Innovations such as single-incision laparoscopic surgery (SILS) and natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in MIS. These techniques further reduce the invasiveness of procedures, offering even greater benefits to patients4.
Expansion of Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, with new robotic systems being developed for various surgical specialties. The integration of robotics with imaging technologies, such as MRI and CT scans, will enable more precise and effective interventions. This expansion will make robotic surgery accessible to a broader range of patients and conditions7.
Conclusion
Minimally invasive surgery represents the future of medical procedures, offering numerous benefits such as reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. With ongoing advancements in technology and surgical techniques, MIS is set to become even more effective and widely adopted. As we look to the future, the integration of AI, development of new instruments, and expansion of robotic surgery will continue to drive the evolution of minimally invasive surgery, improving patient outcomes and transforming the landscape of medical care.